Acupuncture
Acupuncture is (often refers to acupuncture together with moxibustion) is a technique of inserting and manipulating fine filiform needles into specific points on the body with the aim of relieving pain and for therapeutic purposes.According to traditional Chinese medical theory, these acupuncture points lie along meridians along which qi, the vital energy, flows.
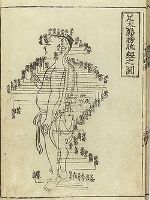 Acupuncture
originated in China and is most commonly associated with traditional Chinese
medicine (TCM). Different types of acupuncture (Classical Chinese, Japanese,
Tibetan, Vietnamese and Korean acupuncture) are practiced and taught
throughout the world. The body of evidence that show its effectiveness is
growing.
Acupuncture
originated in China and is most commonly associated with traditional Chinese
medicine (TCM). Different types of acupuncture (Classical Chinese, Japanese,
Tibetan, Vietnamese and Korean acupuncture) are practiced and taught
throughout the world. The body of evidence that show its effectiveness is
growing.
Most modern acupuncturists use disposable stainless steel needles of fine diameter (0.007" to 0.020", 0.18 mm to 0.51 mm), sterilized with ethylene oxide or by autoclave. These needles are far smaller in diameter (and therefore less painful) than hypodermic injection needles since they do not have to be hollow for purposes of injection. The upper third of these needles is wound with a thicker wire (typically bronze), or covered in plastic, to stiffen the needle and provide a handle for the acupuncturist to grasp while inserting. The size and type of needle used, and the depth of insertion, depend on the acupuncture style being practised.
 Warming
an acupuncture point, typically by moxibustion (the burning of a combination
of herbs, primarily mugwort), is a different treatment than acupuncture
itself and is often, but not exclusively, used as a supplemental treatment.
The Chinese term zhēn jǐu, commonly used to refer to acupuncture, comes from
zhen meaning "needle", and jiu meaning "moxibustion". Moxibustion is used to
varying degrees among current schools of oriental medicine. For example, one
well-known technique is to insert the needle at the desired acupuncture
point, attach dried moxa to the external end of an acupuncture needle, and
then ignite it. The moxa will then smolder for several minutes (depending on
the amount adhered to the needle) and conduct heat through the needle to the
tissue surrounding the needle in the patient's body. Another common
technique is to hold a large glowing stick of moxa over the needles. Moxa is
also sometimes burned at the skin surface, usually by applying an ointment
to the skin to protect from burns, though burning of the skin is general
practice in China.
Warming
an acupuncture point, typically by moxibustion (the burning of a combination
of herbs, primarily mugwort), is a different treatment than acupuncture
itself and is often, but not exclusively, used as a supplemental treatment.
The Chinese term zhēn jǐu, commonly used to refer to acupuncture, comes from
zhen meaning "needle", and jiu meaning "moxibustion". Moxibustion is used to
varying degrees among current schools of oriental medicine. For example, one
well-known technique is to insert the needle at the desired acupuncture
point, attach dried moxa to the external end of an acupuncture needle, and
then ignite it. The moxa will then smolder for several minutes (depending on
the amount adhered to the needle) and conduct heat through the needle to the
tissue surrounding the needle in the patient's body. Another common
technique is to hold a large glowing stick of moxa over the needles. Moxa is
also sometimes burned at the skin surface, usually by applying an ointment
to the skin to protect from burns, though burning of the skin is general
practice in China.
The American Academy of Medical Acupuncture (2004) states: "In the United States, acupuncture has its greatest success and acceptance in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain." They say that acupuncture may be considered as a complementary therapy for the conditions in the list below, noting: "Most of these indications are supported by textbooks or at least 1 journal article."
|
|
|